Vibrio
History:
During the 19th century ,cholera spread across the world wide.The current pandemic started in South Asian in 1961 after reached Africa in 1971and the America's in 1991.
Scientific classification
Domain:Bacteria
Phylum:pseudomonadota
Class:Gammproteobacteria
Order:vibrionales
Family:vibrionaceae
Genum:vibrio
Morphology:
* vibrio is a genus of gram negative curved bacilli.
*They are actively motile by means of polar flagellum.
*The name vibrio is derived from its characteristics vibratory motility
(From vibrare meaning 'to vibrate')
* vibrios are present in marine environments and surface waters worldwide.
*The most important member of the genus is vibrio cholerae.
* The vibrio cholerae is a short curved rods,about 1.5×0.2_0.4MU m.
*pleomorphism is common in old culture.
*In stained films of mucus flakes taken from acute cholerae cases,the vibrios are seen arranged in parallel rows this is described as a' Fish in a stream' appearance.
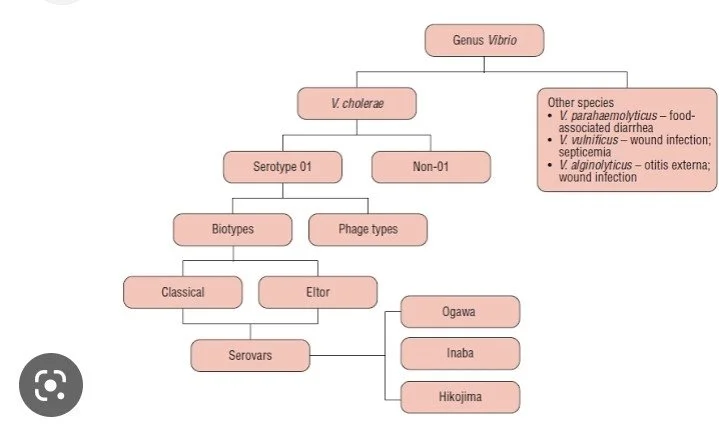
Classification:
Based on their requirement of sodium chloride, vibrios are classified as halophilic and non- halophilic .
*Halophilic: v.parahemolyticus ,v.alginolyticus,v.vulnificus.
*Non-halophilic: vibrio cholerae
Resistance:
* vibrio cholera are susceptible to heat,drying and acids but resist high alkalinity.
*They are killed at 55° c in 15 minutes.
*In clean tap water they survive for thirty days .
* In untreated soil,they may survive for several days.
* On fruits, they survive for 1-5 days at room temperature and for a week in the refrigerator.
*vibrio cholera killed in gastric juice with in few minutes.
Symptoms:
* high fever
* weight loss
*feeling of nausea
* bloating in the belly
*blood pressure becomes low
Adapted from: public health notes.com
Pathogenesis:
* The vibrio cholera remain in the gut and does not multiply into the blood stream.
*It adheres to the mucosa of the small intestines by both outer membrane protein and flagella adhesions.
*vibrio cholera produces enterotoxin that causes excessive fluid and electrolyte loss.
*sodium chloride aborsorption is inhibited and therefore excreted resulting in water ,sodium chloride and potassium bicarbonate loss.
Lab diagnosis:
Specimen collection and transport
* Stool specimens suspected of containing vibrio species should be collected and transported only in the cairy Blair medium.
*Buffered glycerol medium is not acceptable because in vibrio glycerol is toxic.
*Feces is preferable ,but rectal swabs are acceptable during the acute phase of diarrheal illness.
Direct Detection Method
*vibrio cholera toxin can be detected in stool using an enzyme linked assay (ELISA)or latex agglutination test.
* when stool specimens are examined using a dark field microscopy , the bacilli exhibit characteristics rapid darting ( or) shooting star motility
Treatment:
* Rehydration
- IV lactated Ringer's ( L R)
-ORS : by mouth (or) by N G tube
-Zinc supplement
* Antibiotics
Adults : Deoxycycline 300 mg PO×1
Children or pregnant women: TMP-SMX ×3 days
Adapted from: Hind pharma
Prevention:
*Drink boiled water.
* Avoid consumption of raw foods.
*Avoid dairy products as much as possible .
*Wash your hands with soap.
* Wash fruits and vegetables before you eat.
* Drink plenty of water.
References :
1. Ananthanarayan and Paniker's textbook of microbiology
2.vibrio A presentation by Dr ALPANA VERMA International medical and Technological University, Tanzania
3.cholera By JAMES NYIRENDA